Goals
Upon successful completion of this lab, you should be able to write and edit Python programs that use:
- numeric data types
- arithmetic operations
- order of operations
- the math library
Setup and Practice
Setup
- Before you start writing code, you will set up a directory for this assignment on the blue server. Follow these procedures to mount your blue home-directory on the local machine.
- Once you have mounted your blue home directory on the local machine, create a folder called cs115.
- Create a folder called lab02 inside the folder called cs115.
- Now, launch PyCharm and create a new project inside the lab02 folder, which is inside cs115 which is in your blue home directory.
Practice
- Answer Questions 1-5 in your writeup (on Moodle). Click "Check" after you answer each question to check and save your work.
- In a new browser tab, visit
the online Python 3 tutor
and enter the following Python code:
x = "I" y = 'see' x = "what" x = 'you' y = "did there!"
Then click "Visualize execution." - You should now see your code at the top left of the window. The next instruction to be executed is highlighted. Try clicking the "Forward" button once. Your program's output will be displayed in the window just below your program, and the current values of your variables will be displayed on the right.
- Slowly click "Forward", and watch as each statement is executed in order. Pay attention to the values of your variables and how they change.
- Try to answer Question 6 in your Moodle writeup based on what you observed. If you get stuck, you can click the "First" button in the Online Python Tutor to restart the visualization.
- Continue to Part A.
Part A: Computing the area of a square
The instructions below will help you write a program that:
- Asks the user to enter the side length for a square.
- Calculates the area of the square.
- Prints that calculated area.
You should be able to trace through the execution of this program and understand how the values of the variables change after each statement.
Instructions
- First, in PyCharm, create a file called lab02.py in project cs115/lab02.
- Type (or copy-paste) the following program exactly as written, substituting your name for the italicized text:
""" Program: CS 115 Lab 2 Author: Your name Description: This program will compute the area of a square, given the side length. """ def main(): # Get the side length length = float(input('Enter a numeric value: ')) # Compute the area of the square square_area = length * length print("The area of a square with side length ", length, " is ", square_area, ".", sep="") main() - Execute the program several times to complete the table in Question 7 of your Moodle writeup.
- Each time you execute the program, you will be prompted to enter a value. When that happens, type in the information from one of the rows, exactly as it appears in the Input Value column, and then press the enter key.
- Record the value that your program reports for the area of the square.
- Continue to Part B.
Part B: Computing the area of a circle
In this part of the lab, you will extend your program from Part A to compute the area of a circle, given the length of the radius.
Recall that the area of a circle with radius r can be calculated as
A = π * r2
Your new program will ask the user for only one numeric value. Then, it will use that value to compute the areas of both the circle and the square.
Here is a sample of what your revised program will do. The user's input is italicized and underlined.
Enter a numeric value: 10 The area of a square with side length 10.0 is 100.0. The area of a circle with radius length 10.0 is 314.159.
Note: For full credit in the lab, your output will have to match the final sample outputs exactly.
Instructions
Since you are extending your program, do not delete any of your existing code as you follow the instructions below! Throughout the lab, we will just keep extending the same program, adding more and more functionality.
- To do your computation, you should use the definition of π from the math library. To do this, import the math library using an
import mathstatement. Place this statement early in your program (after the program's docstring and beforedef main()):import math
- From now on, you will be able to use the constant
math.pi
whenever you need the value of π for a calculation. - In your current program, notice that the statement
square_area = length * length
computes the area of a square whose side length islengthand saves the result in a variable calledsquare_area. - Just after that statement, add a similar statement to your program to calculate the area of a circle whose radius length is also
length. Your statement should store the result of this calculation in a new variable with an appropriate name. - After your current print statement, add a statement to the program to print the area of the circle. This statement should be similar to the
printstatement that prints the area of the square, but be sure to change the wording to match the sample output above. - Update the docstring at the top of your program so that it accurately describes what the program does. Make sure that it lists you as the author of the program.
- Run your program, typing in the number 10 when prompted. Compare your results with the output below:
Enter a numeric value: 10 The area of a square with side length 10.0 is 100.0. The area of a circle with radius length 10.0 is 314.159. Modify your program to make sure it matches the sample output above, exactly. It may be the case that your output looks different compared to the above. If so, employ the below guidance to make it match.
First, if the decimal places of the area of a square do not match: it may be that variable
lengthholds anint, when it makes more sense to let its value be afloat. Adjust your code so that variablelengthholds the correct type of value.Second, if the decimal places of the area of a circle do not match: it may just be that the computer you are on has a different floating point accuracy, and you need to round the value to match the output. The
round()function is used to round numeric values. For example, the below code rounds the value 2.6753 to 2 decimal places, and produces the output The value is 2.68.print("The value is", round(2.6753, 2))- If you have not done so already, click "Next" in your Moodle writeup to advance to Question 8.
- Execute the program several times to complete the table in Question 8 of your Moodle writeup.
- Each time you execute the program, you will be prompted to enter a value. When that happens, type in the information in a row of the Input Value column, exactly as it appears, then press enter.
- Record the value that your program reports for the area of the circle. The area of the square should be the same as before.
- Continue to Part C.
Part C: Computing the volume of a cube
In this part of the lab, we will extend our program from Part B, to compute the volume of a cube, given the length of the edge.
Recall that the volume of a cube with edge length e can be calculated as
V = e3.
Here is a sample of what your revised program will do. The user's input is italicized and underlined.
Enter a numeric value: 10 The area of a square with side length 10.0 is 100.0. The area of a circle with radius length 10.0 is 314.159. The volume of a cube with edge length 10.0 is 1000.0.
Instructions
Continue working on lab02.py using PyCharm. Remember: not to delete any of the existing code. Also, do not prompt the user to enter another value.
- Just after the other calculations, add a line to the program to calculate the volume of a cube whose edge length is
length. Store the result of this calculation in a new variable with an appropriate name. - Add a line to the program to print the volume of the cube. Be sure the wording matches the sample output exactly.
- Run your program. Make sure it matches the example below:
Enter a numeric value: 10 The area of a square with side length 10.0 is 100.0. The area of a circle with radius length 10.0 is 314.159. The volume of a cube with edge length 10.0 is 1000.0. - Run your program. Record the volumes of the cubes in Question 9 of your writeup.
- Continue to Part D.
Part D: Computing the volume of a sphere
In this part of the lab, we will extend our program from Part C, to compute the volume of a sphere, given the length of the radius.
Recall that the volume of a sphere with radius r can be calculated as:
V = 4/3 * π * r3
Here is a sample of what your revised program will do. The user's input is italicized and underlined.
Enter a numeric value: 10 The area of a square with side length 10.0 is 100.0. The area of a circle with radius length 10.0 is 314.159. The volume of a cube with edge length 10.0 is 1000.0. The volume of a sphere with radius length 10.0 is 4188.79.
Instructions
Continue working on lab02.py using PyCharm. Remember: not to delete any of the existing code. Also, do not prompt the user to enter another value.
- Just after the other calculations, add a line to the program to calculate the volume of a sphere whose radius length is
length. Store the result of this calculation in a new variable with an appropriate name. - Add a line to the program to print the volume of the sphere. Be sure the wording matches the sample output.
- Run your program. Make sure it matches the example:
Enter a numeric value: 10 The area of a square with side length 10.0 is 100.0. The area of a circle with radius length 10.0 is 314.159. The volume of a cube with edge length 10.0 is 1000.0. The volume of a sphere with radius length 10.0 is 4188.79.
- Run your program. Record the volumes of the spheres in Question 10 of your writeup.
- Continue to Part E.
Part E: Computing the area of an equilateral triangle
In this part of the lab, we will extend our program from Part D, to compute the area of an equilateral triangle, given the length of a side.
Recall that the area of an equilateral triangle with side s is:
s2 * (square root of 3) / 4
Here is a sample of what your revised program will do. The user's input is italicized and underlined.
Enter a numeric value: 10 The area of a square with side length 10.0 is 100.0. The area of a circle with radius length 10.0 is 314.159. The volume of a cube with edge length 10.0 is 1000.0. The volume of a sphere with radius length 10.0 is 4188.79. The area of an equilateral triangle with side length 10.0 is 43.301.
Instructions
Continue working on lab02.py using PyCharm. Remember: not to delete any of the existing code. Also, do not prompt the user to enter another value.
- Just after the other calculations, add a line to the program to calculate the area of an equilateral triangle whose side length is
length. Store the result of this calculation in a new variable with an appropriate name. Hint:math.sqrt(x)will compute the square root of the value stored in variable x. - Add a line to the program to print the area of the equilateral triangle. Be sure the wording matches the sample output exactly.
- Run your program. Make sure it matches the example:
Enter a numeric value: 10 The area of a square with side length 10.0 is 100.0. The area of a circle with radius length 10.0 is 314.159. The volume of a cube with edge length 10.0 is 1000.0. The volume of a sphere with radius length 10.0 is 4188.79. The area of an equilateral triangle with side length 10.0 is 43.301.It should match in terms of spelling, capitalization, white-space and decimal precision. If your output's decimal places do not match the above, then review the guidance from Part B on how to match the decimal output. - Run your program. Record the areas of the triangles in Question 11 of your writeup.
- Update your docstring to reflect what your program is doing now.
- Demo. Call an instructor or lab assistant over to demo your program.
- Continue to the next part.
Assignment Submission
Instructions
- Answer Question 12 in your Moodle writeup. Review your answers, and then click the "Next" button at the bottom of the quiz. Once you do that, you should see a "Summary of Attempt" screen.
Click the "Submit all and finish" button. Warning: You must hit "Submit all and finish" so that your writeup can be graded! It is not submitted until you do this. Once you have submitted your quiz, you should see should see a dialog box similar to one shown below. The important part is that the "State" is recorded as Finished.
Please leave this window up as a tab in your browser.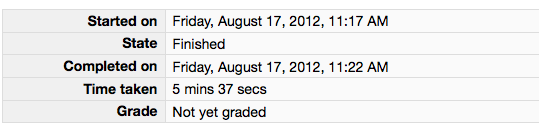
- Click on the "Lab 2 code" link in Moodle and open in a new tab. Follow the instructions to upload your source code (lab02.py) for Lab02. You could either browse for your code or, using a finder window, drag and drop your lab02.py from your cs115/lab02 folder to Moodle. You should subsequently see a dialog box which indicates 'Submission Status' as 'Submitted for grading'. Leave this tab open in you browser.
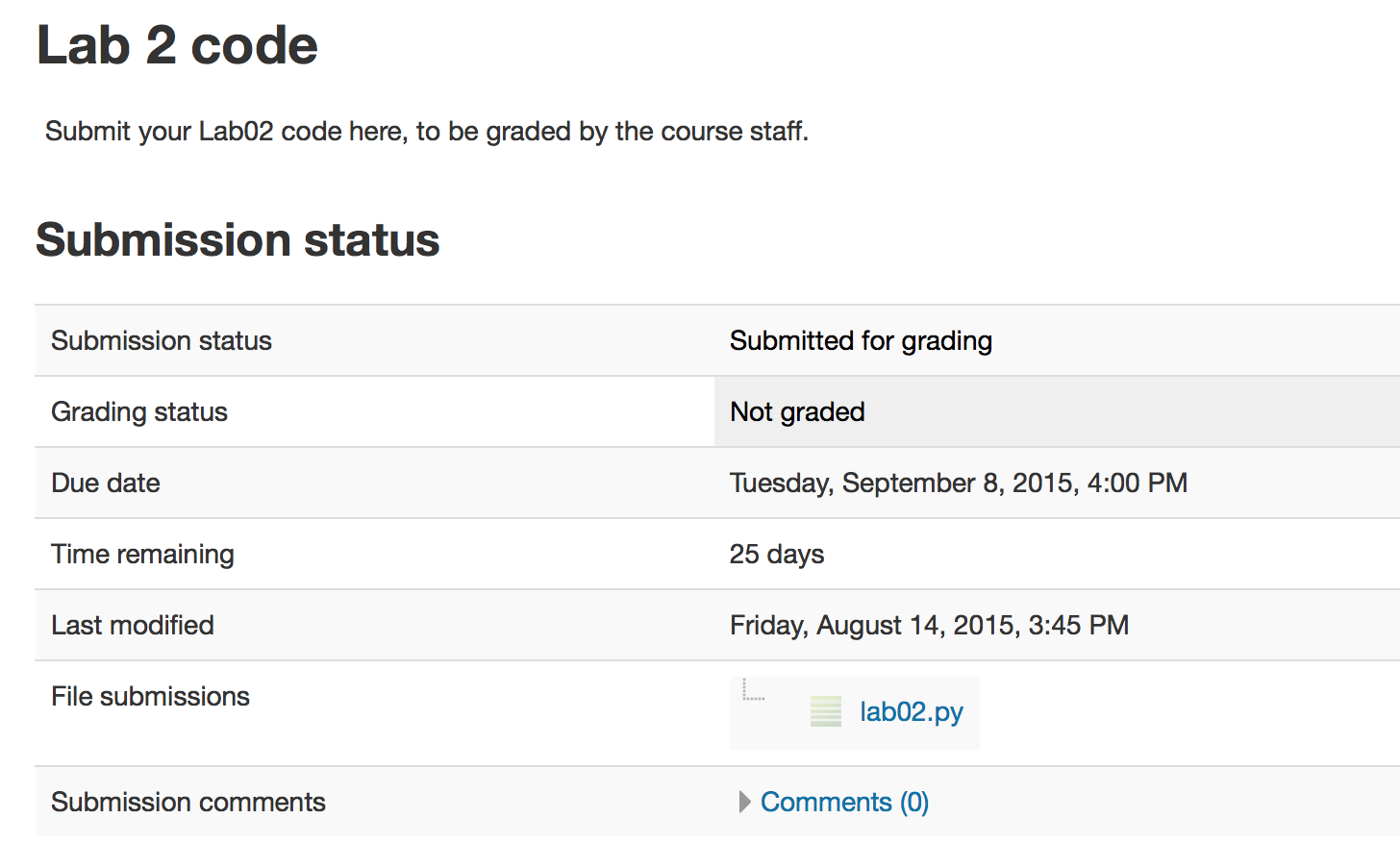
- With these confirmation pages open in your browser, you may call an instructor over to verify that you have completed every part of the lab. Otherwise, you are done!